浅谈Java代理(Proxy)
代理模式
利用代理可以在运行时创建一个实现了一组给定接口的新类。这种功能只有在编译时无法确定需要实现那个接口时才有必要使用。
——摘自《JAVA核心技术卷I》
何时使用代理?
假设有一个表示接口的Class对象(有可能只包含一个接口),它的确切类型在编译时无法知道。这确实有些难度。想要构造一个实现这些接口的类,就需要使用newInstance方法或反射找出这个类的构造器。但是,不能实例化一个接口,需要在程序处于运行状态时定义一个新类。 为了解决这个问题,有些程序将会生成代码;将这西代码放置在一个文件中;调用编译器;然后再加载结果类文件。很自然,这样做的速度会比较慢,并且需要将编译器与程序放在一起。而代理机制则是一种更好的解决方案。代理类可以在运行时创建全新的类。这样的代理类能够实现指定的接口。
——摘自《JAVA核心技术卷I》
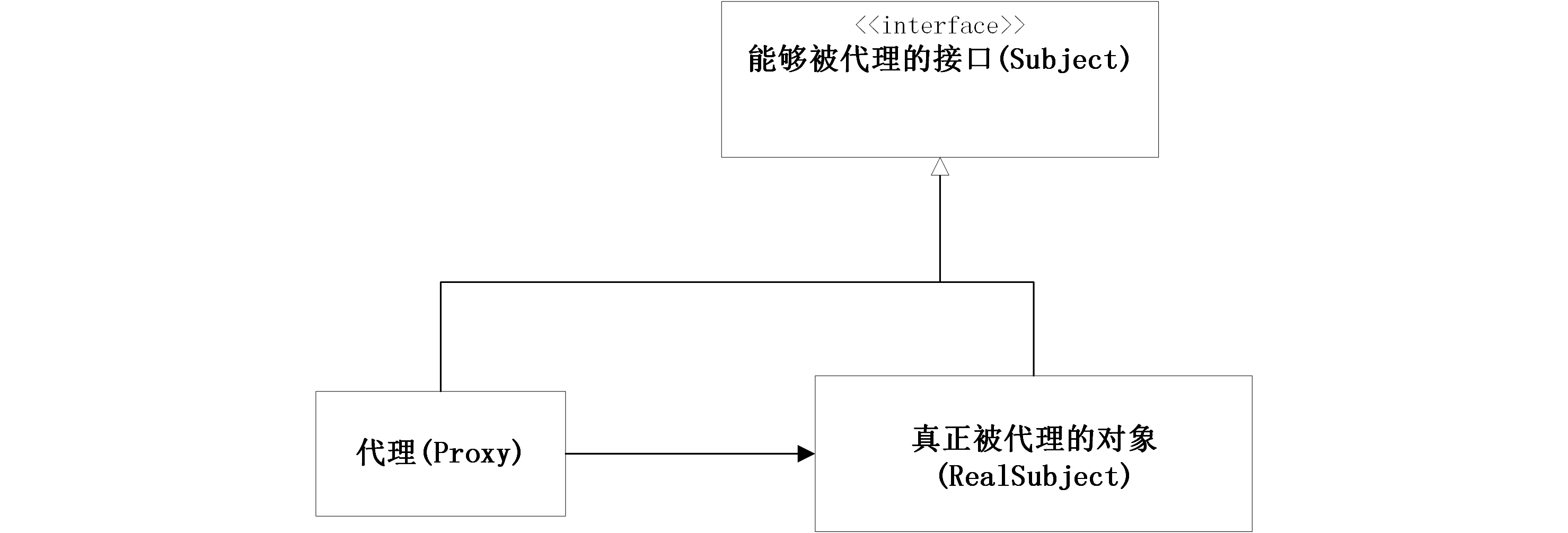
代理模式中主要有三个要素:
Subject(被代理的接口).声明了代理对象和真实对象的公共接口.即定义了程序要实现哪些行为.RealSubject(真正被代理的对象).即真实对象,是代理对象所表示的真实对象,也就是最终被引用的对象.真实对象继承于接口,真正提供一些服务.Proxy(代理).可以看做代理对象,当访问真实对象时,需要通过代理去访问。
也即:
- 用户只关心接口功能,而不在乎谁提供了功能。上图中接口是 Subject。
- 接口真正实现者是上图的 RealSubject,但是它不与用户直接接触,而是通过代理。
- 代理就是上图中的 Proxy,由于它实现了 Subject 接口,所以它能够直接与用户接触。
- 用户调用 Proxy 的时候,Proxy 内部调用了 RealSubject。所以,Proxy 是中介者,它可以增强 RealSubject 操作。
- 代理和真实对象必须继承同一个接口.
- 代理对象必须包含真实的对象.
如果难于理解的话,我用事例说明好了。值得注意的是,代理可以分为静态代理和动态代理两种。先从静态代理讲起。
静态代理
电影开始前会播放一些广告,电影是电影公司委托给影院进行播放的,但是影院可以在播放电影的时候,产生一些自己的经济收益,比如卖爆米花、可乐等,然后在影片开始结束时播放一些广告。
现在用代码来进行模拟。 根据第一节中介绍的,代理模式要有三个要素:Subject、RealSubject、Proxy.
首先得有一个接口,通用的接口是代理模式实现的基础。这个接口我们命名为 Movie,代表电影播放的能力。
public interface Movie {
void play();
}
然后要有一个真正的实现这个 Movie 接口的类.这个类表示真正的影片。它实现了 Movie 接口,当play() 方法调用时,影片就开始播放。
public class RealMovie implements Movie {
@Override
public void play() {
System.out.println("You are watching Avengers4");
}
}
然后需要一个实现接口的代理类。Cinema 就是 Proxy 代理对象,前面提到代理对象必须包含真实的对象,Cinema对象中就有一个RealMovie对象。它有一个 play() 方法。不过调用 play() 方法时,它进行了一些相关利益的处理,那就是广告。现在,我们编写测试代码。
public class Cinema implements Movie {
private RealMovie movie;
public Cinema(RealMovie movie){
super();
this.movie = movie;
}
@Override
public void play() {
playAdvertisement(true);
movie.play();
playAdvertisement(false);
}
private void playAdvertisement(boolean isStart) {
if( isStart ){
System.out.println("The film will be on at once.This is an advertisement!");
}
else{
System.out.println("The film is over.This is an advertisement!");
}
}
}
测试代码:
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
RealMovie realmovie = new RealMovie();
Movie movie = new Cinema(realmovie);
movie.play();
}
}
测试结果:
The film will be on at once.This is an advertisement!
You are watching Avengers4
The film is over.This is an advertisement!
代理模式可以在不修改被代理对象的基础上,通过扩展代理类,进行一些功能的附加与增强。值得注意的是,代理类和被代理类应该共同实现一个接口,或者是共同继承某个类。
上面介绍的是静态代理的一个示例,为什么叫做静态呢?因为它的类型是事先预定好的,比如上面代码中的 Cinema 这个类。下面要介绍的内容就是动态代理。
动态代理
动态代理的代理类并不需要在Java代码中定义,而是在运行时动态生成的。相比于静态代理, 动态代理的优势在于可以很方便的对代理类的函数进行统一的处理,而不用修改每个代理类的函数。通过使用动态代理,可以做一个“统一指示”,对所有代理类的方法进行统一处理,而不用逐一修改每个方法。
与静态代理相比,抽象角色、真实角色都没有变化。变化的只有代理类。
上一节代码中 Cinema 类是代理,需要手动编写代码让 Cinema 实现 Movie 接口,而在动态代理中,我们可以让程序在运行的时候自动在内存中创建一个实现 Movie 接口的代理,而不需要去定义 Cinema 这个类。这就是它被称为动态的原因。
还是使用上面的例子
Subject:
public interface Movie {
void play();
}
RealSubject,我们播放的电影为《复仇者联盟4》:
public class Avengers4 implements Movie {
@Override
public void play() {
System.out.println("You are watching Avengers4");
}
}
关键的不同在于代理类的实现,在使用动态代理时,需要定义一个位于代理类与委托类之间的中介类,也叫动态代理类,这个类被要求实现InvocationHandler接口.:
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Cinema implements InvocationHandler {
private Object moive;
public Cinema(Object moive){
this.moive = moive;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("This is "+ this.getClass().getSimpleName() +".The film will be on at once.");
method.invoke(moive,args);
System.out.println("The film is over.");
return null;
}
}
当调用代理类对象的方法时,这个“调用”会转送到中介类的invoke方法中,参数method标识了具体调用的是代理类的哪个方法,args为这个方法的参数。
进行测试:
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
//要代理的真实对象
RealMovie realmovie = new RealMovie();
//创建中介类实例
InvocationHandler cinema = new Cinema(realmovie);
//动态产生一个代理类
Movie dynamicProxyOfMovie = (Movie) Proxy.newProxyInstance(realmovie.getClass().getClassLoader(),
realmovie.getClass().getInterfaces(),
cinema);
//通过代理类,执行doSomething方法
dynamicProxyOfMovie.play();
}
}
测试结果:
This is Cinema.The film will be on at once.
You are watching Avengers4
The film is over.
在上面动态代理的例子中,并没有像静态代理那样为 Moive 接口实现一个代理类,但最终它仍然实现了相同的功能,这其中的差别,就是之前讨论的动态代理所谓“动态”的原因。 一个典型的动态代理可分为以下四个步骤:
- 创建抽象角色(Movie)
- 创建真实角色(Avengers4)
- 通过实现InvocationHandler接口创建中介类(Cinema)
- 通过场景类,动态生成代理类
动态代理语法
Proxy
动态代理对象,使用Proxy的静态方法newProxyInstance方法。
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
这个方法有三个参数:
- 一个类加载器(class loader).
- 一个Class对象数组,每个元素都是需要实现的接口.
- 一个调用处理器.
InvocationHandler
InvocationHandler 是一个接口,官方文档解释说,每个代理的实例都有一个与之关联的 InvocationHandler 实现类,如果代理的方法被调用,那么代理便会通知和转发给内部的 InvocationHandler 实现类,由它决定处理。
public interface InvocationHandler {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable;
}
invoke方法中的三个参数:
- proxy 代理对象.即我们上面的
RealMovie - method 代理对象调用的方法
- args 调用的方法中的参数
无论何时调用代理对象的方法,调用处理器的invoke方法都会被调用,并向其传递Method对象和原始的调用参数。调用处理器必须给出处理调用的方式。
——摘自《JAVA核心技术卷I》
正是这个方法决定了怎么样处理代理传递过来的方法调用。 因为 Proxy 动态产生的代理会调用 InvocationHandler 实现类,所以 InvocationHandler 是实际执行者。
那么实际生活中,电影院中不仅播放《复仇者联盟4》,还会播放其他电影。比如我们播放《黑客帝国(The Matrix)》
创建类TheMatrix:
public class TheMatrix implements Movie {
@Override
public void play() {
System.out.println("You are watching The Matrix.");
}
}
那么电影院同样播放电影《黑客帝国》,它也在同一个电影院播放。
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
Avengers4 avengers4 = new Avengers4();
TheMatrix theMatrix = new TheMatrix();
InvocationHandler cinemaWanDa = new Cinema(avengers4);
InvocationHandler cinemaWanDa1 = new Cinema(theMatrix);
Movie dynamicProxyAvengers = (Movie) Proxy.newProxyInstance(avengers4.getClass().getClassLoader(),
avengers4.getClass().getInterfaces(),
cinemaWanDa);
Movie dynamicProxyTheMatrix = (Movie) Proxy.newProxyInstance(theMatrix.getClass().getClassLoader(),
theMatrix.getClass().getInterfaces(),
cinemaWanDa1);
dynamicProxyAvengers.play();
dynamicProxyTheMatrix.play();
}
}
运行结果:
This is Cinema.The film will be on at once.
You are watching Avengers4
The film is over.
This is Cinema.The film will be on at once.
You are watching The Matrix.
The film is over.
假设此时正值世界杯期间,电影院开通了观看球赛的服务。 首先和电影一样,创建一个球赛的接口(Subject).
public interface WorldCup {
void watchTheMatch();
}
这时候需要一个RealSubject,假设我们观看法国和西班牙的比赛:
public class FrenchVSSpain implements WorldCup {
@Override
public void watchTheMatch() {
System.out.println("You are watching French VS Spain");
}
}
然后进行测试:
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
Avengers4 avengers4 = new Avengers4();
TheMatrix theMatrix = new TheMatrix();
FrenchVSSpain frenchVSSpain = new FrenchVSSpain();
InvocationHandler cinemaWanDa = new Cinema(avengers4);
InvocationHandler cinemaWanDa1 = new Cinema(theMatrix);
InvocationHandler cinemaWanda2 = new Cinema(frenchVSSpain);
Movie dynamicProxyAvengers = (Movie) Proxy.newProxyInstance(avengers4.getClass().getClassLoader(),
avengers4.getClass().getInterfaces(),
cinemaWanDa);
Movie dynamicProxyTheMatrix = (Movie) Proxy.newProxyInstance(theMatrix.getClass().getClassLoader(),
theMatrix.getClass().getInterfaces(),
cinemaWanDa1);
dynamicProxyAvengers.play();
dynamicProxyTheMatrix.play();
WorldCup dynamicProxyFVSS = (WorldCup) Proxy.newProxyInstance(frenchVSSpain.getClass().getClassLoader(),
frenchVSSpain.getClass().getInterfaces(),
cinemaWanda2);
dynamicProxyFVSS.watchTheMatch();
}
}
测试结果:
This is Cinema.The film will be on at once.
You are watching Avengers4
The film is over.
This is Cinema.The film will be on at once.
You are watching The Matrix.
The film is over.
This is Cinema.The film will be on at once.
You are watching French VS Spain
The film is over.
同样是通过 Proxy.newProxyInstance() 方法,却产生了 Movie 和 WorldCup 两种接口的实现类代理,这就是动态代理的强大之处。
动态代理的秘密
Proxy 能够动态产生不同接口类型的代理,是通过传递的接口,然后通过反射动态生成了一个接口实例。
Proxy的全部源码查看点击这里
newProxyInstance()方法:
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
/*
* Look up or generate the designated proxy class.
*/
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
/*
* Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler.
*/
try {
if (sm != null) {
checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl);
}
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
final InvocationHandler ih = h;
if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
cons.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
} catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
} else {
throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
}
}
Proxy类的newProxyInstance方法,主要业务逻辑如下:
//生成代理类class,并加载到jvm中
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, interfaces);
//获取代理类参数为InvocationHandler的构造函数
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
//生成代理类,并返回
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
上面代码做了三件事:
-
根据传入的参数interfaces动态生成一个类,它实现interfaces中的接口,该例中即Movie接口的play方法。假设动态生成的类为$Proxy0。
- 通过传入的classloder,将刚生成的$Proxy0类加载到jvm中。
- 利用中介类,调用 $Proxy0的$Proxy0(InvocationHandler)构造函数,创建$Proxy0类的实例,其InvocationHandler属性,为我们创建的中介类。
newProxyInstance 方法创建了一个实例,它是通过 cl 这个 Class 文件的构造方法反射生成。cl 由 getProxyClass0() 方法获取。 上面的核心,就在于getProxyClass0方法:
private static Class<?> getProxyClass0(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>... interfaces) {
if (interfaces.length > 65535) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded");
}
// If the proxy class defined by the given loader implementing
// the given interfaces exists, this will simply return the cached copy;
// otherwise, it will create the proxy class via the ProxyClassFactory
return proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces);
}
在Proxy类中有个属性proxyClassCache,这是一个WeakCache类型的静态变量。它指示了类加载器和代理类之间的映射。所以proxyClassCache的get方法用于根据类加载器来获取Proxy类,如果已经存在则直接从cache中返回,如果没有则创建一个映射并更新cache表。
直接通过缓存获取,如果获取不到,注释说会通过 ProxyClassFactory 生成。(这里就不贴ProxyClassFactory方法的全部源码,可以去上面的连接查看)
ProxyClassFactory的部分源码:
/**
* A factory function that generates, defines and returns the proxy class given
* the ClassLoader and array of interfaces.
*/
private static final class ProxyClassFactory
implements BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>>
{
// prefix for all proxy class names
private static final String proxyClassNamePrefix = "$Proxy";
...
/*
* Choose a name for the proxy class to generate.
*/
long num = nextUniqueNumber.getAndIncrement();
String proxyName = proxyPkg + proxyClassNamePrefix + num;
...
/*
* Generate the specified proxy class.
*/
byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(
proxyName, interfaces, accessFlags);
try {
return defineClass0(loader, proxyName,
proxyClassFile, 0, proxyClassFile.length);
} catch (ClassFormatError e) {
/*
* A ClassFormatError here means that (barring bugs in the
* proxy class generation code) there was some other
* invalid aspect of the arguments supplied to the proxy
* class creation (such as virtual machine limitations
* exceeded).
*/
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e.toString());
}
}
这个类的注释说,通过指定的 ClassLoader 和 接口数组 用工厂方法生成 proxy class。 然后这个 proxy class 的名字是:包名+$Proxy+id序号
跟一下代理类的创建流程: 调用Factory类的get方法,而它又调用了ProxyClassFactory类的apply方法,最终找到下面一行代码:
byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(
proxyName, interfaces, accessFlags);
就是它,生成了代理类。
下面检测检测一下动态生成的代理类的名字是不是包名+$Proxy+id序号,在测试类中添加如下代码:
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
...
System.out.println("dynamicProxyAvengers class name:"+dynamicProxyAvengers.getClass().getName());
System.out.println("dynamicProxyTheMatrix class name:"+dynamicProxyTheMatrix.getClass().getName());
System.out.println("dynamicProxyFVSS class name:"+dynamicProxyFVSS.getClass().getName());
}
}
测试结果:
This is Cinema.The film will be on at once.
You are watching Avengers4
The film is over.
This is Cinema.The film will be on at once.
You are watching The Matrix.
The film is over.
This is Cinema.The film will be on at once.
You are watching French VS Spain
The film is over.
dynamicProxyAvengers class name:com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0
dynamicProxyTheMatrix class name:com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0
dynamicProxyFVSS class name:com.sun.proxy.$Proxy1
Movie 接口的代理类名是:com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0 WorldCup 接口的代理类名是:com.sun.proxy.$Proxy1 这说明动态生成的 proxy class 与 Proxy 这个类同一个包。
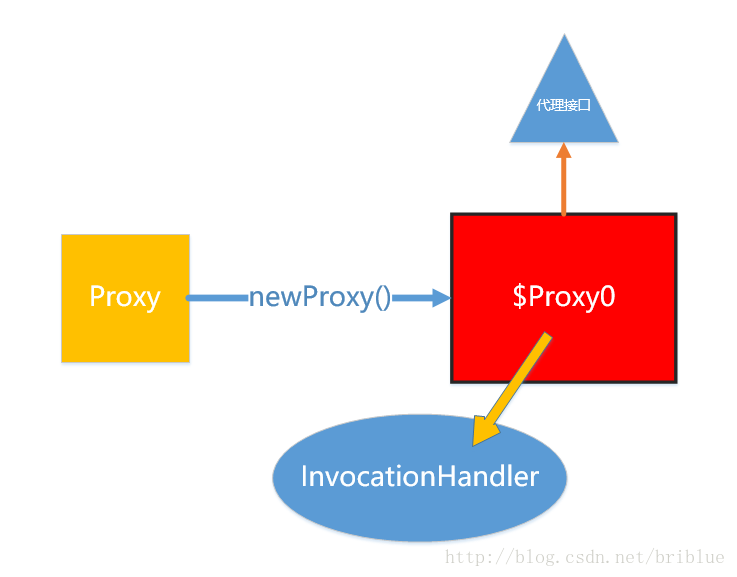
图片来自 https://blog.csdn.net/briblue/article/details/73928350
红框中 $Proxy0就是通过 Proxy 动态生成的。 $Proxy0实现了要代理的接口。 $Proxy0通过调用 InvocationHandler来执行任务。
代理的作用
主要作用,还是在不修改被代理对象的源码上,进行功能的增强。
这在 AOP 面向切面编程领域经常见。
代理类是在程序运行过程中创建。然而一旦被创建,就变成了常规类,与虚拟机中的任何其他类没有什么区别。 所有的代理类都拓展于Proxy类。一个代理类只有一个实例域——调用处理器,它定义在Proxy的超类中。为了履行代理对象的职责,所需要的任何附加数据都必须存储在调用处理器中。
例如上面我们代理Avengers4对象时,Cinema包装了实际的对象。(因为电影要在电影院播放)。
没有定义代理类的名字,Sun虚拟机中的Proxy类将生成一个以字符串$Proxy开头的类名。 对于特定的类加载器和预设的一组接口来说,只能有一个代理类。也就是说,如果使用同一个类加载器和接口数组调用两次newProxyInstance方法的话,那么只能够得到同一个类的两个对象,也可以利用getProxyClass方法获得这个类:
Class proxyClass = Proxy.getProxyClass(null,interfaces);代理类一定是public和final。如果代理类实现的所有接口都是pubic,代理类就不属于某个特定的包;否则,所有非公有的接口都必须属于同一个包,同时,代理类也属于这个包。
总结
上面的例子可以用下图来概括。
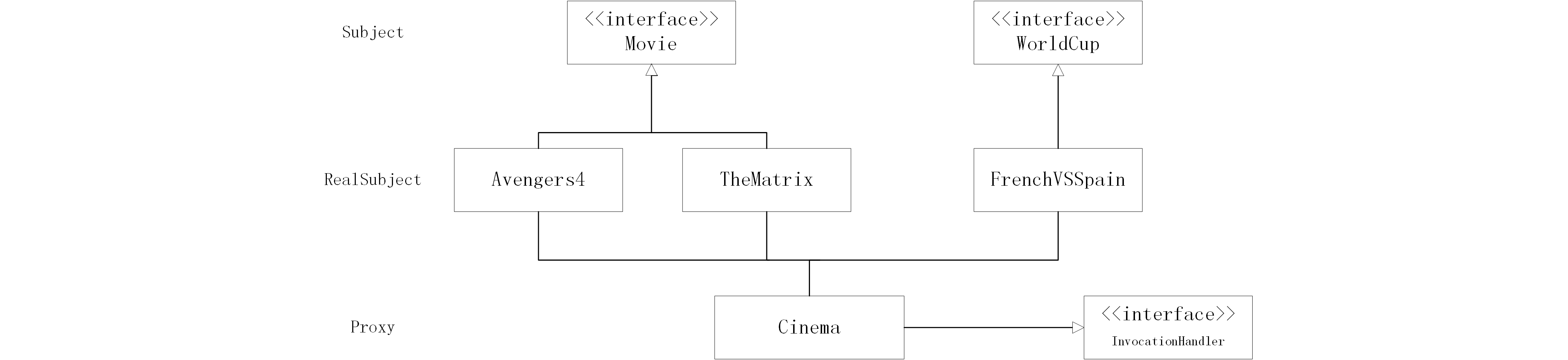
- 代理分为静态代理和动态代理两种。
- 静态代理,代理类需要自己编写代码写成。
- 动态代理,代理类通过 Proxy.newInstance() 方法生成。 不管是静态代理还是动态代理,代理与被代理者都要实现两样接口,它们的实质是面向接口编程。
- 静态代理和动态代理的区别是在于要不要开发者自己定义 Proxy 类。
- 动态代理通过 Proxy 动态生成 proxy class,但是它也指定了一个 InvocationHandler 的实现类。
- 代理模式本质上的目的是为了增强现有代码的功能。